Short Circuit
A short circuit occurs when two or more current-carrying conductors of different phases or different voltage levels or different terminal (in DC circuits) come in contact with each other or with the ground. It is an abnormal condition during which current shoots up several times the permissible limits. Read about short circuits in detail.
A Short circuit, by definition, is an electric circuit that bypass the actual circuit of current flow, offering negligible impedance path to the current flow.
Overload
Overload is an abnormal situation during which the current drawn by the load exceeds the current that can be supplied by the source. In the case of electric motors, overload is a situation at which the load inertia at the motor shaft is higher than the load inertia that the motor can drive.
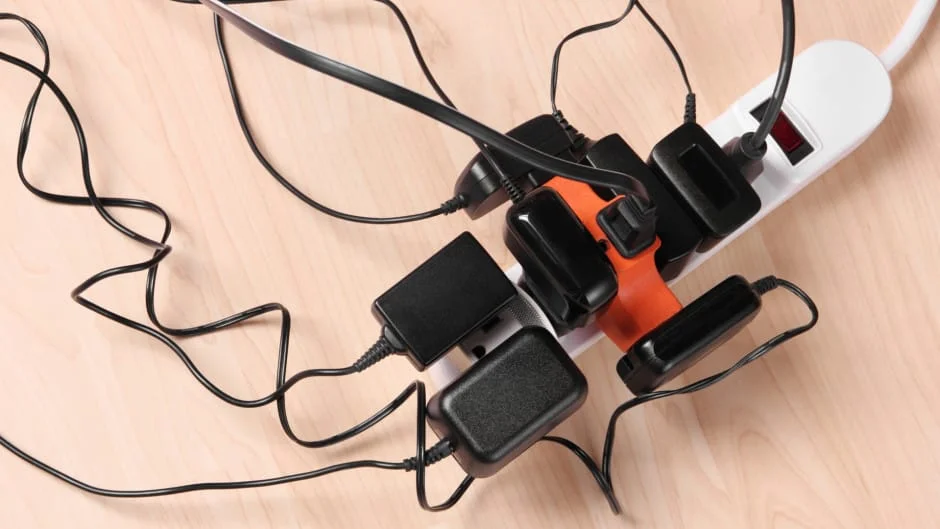

An electric overload, by definition, is a situation during which the load drains more current than the desired value.
Difference between Short circuit and overload
Short circuit and overload, in spite of similarities, are different from each other. On the occurrence of a short circuit, the voltage at the point of the fault falls to zero and the current in the network increases abnormally to a higher value. But in the case of overload reduction in the terminal voltage of the equipment occurs but the voltage will never fall to zero. Similarly, the current also increases to a higher value but not as high as in the case of short circuit.
Comparison of overload and short circuit
| Overload | Short Circuit | |
| Definition | An electric overload, by definition, is a situation during which the load drains more current than the desired value. | An electric circuit that bypasses the actual circuit of current flow, offering negligible impedance path to the current flow. |
| Nature of current | Higher than the rated value. | Several times the rated value. |
| Nature of voltage | Many reduce but does not fall to zero. | Voltage during short circuit drops to zero. |
How to protect against overload and short circuit?
Fuses and circuit breakers are used to safeguard a circuit from overload and short circuits. These devices senses the increase in current flow and breaks the current flow. Thus greater damages are prevented. There are different types of circuit breakers available in the market. HRC fuses, semiconductor fuses, MCBs, ACBs etc are few examples for circuit protection devices.
Great work, my friends. Thank you is very much.
I understood the concepts very well. The difference between Short circuit and overload very much clear to me know. I am following the page from now.
It is really help full for me ! Thanks for writing👍👍👍👍I agree with you partner