Gate turn-off thyristors (GTO) and Silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR) are semiconductor switching devices used in converters, rectifiers, charging circuits, etc. in order to control the current flow. This article illustrates the key differences between GTO and SCR.
What is an SCR?
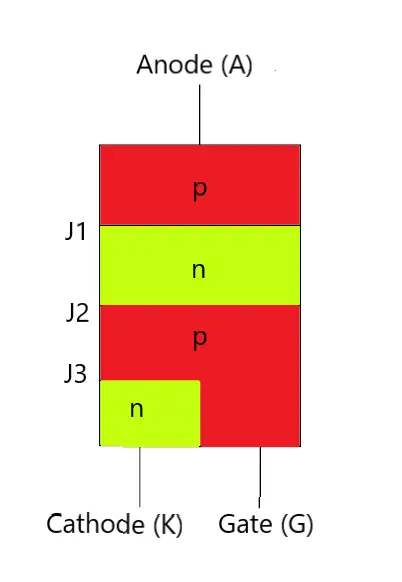
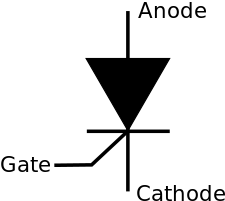
An SCR is a unidirectional semiconductor device that can be triggered into conduction by applying a positive current to its gate terminal. It does not allow reverse conduction and cannot be turned off by applying any type of signal to the gate. The structure and symbol of an SCR are shown below:
What is a GTO?
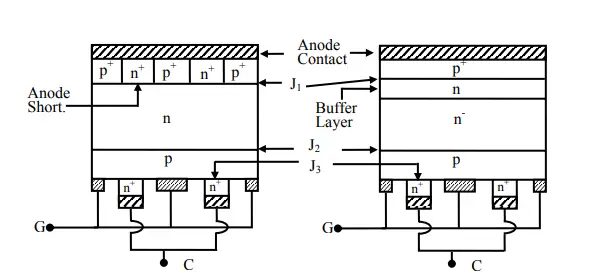
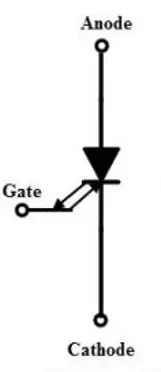
A Gate turn-off thyristor is also a unidirectional semiconductor device that is turned on by applying a small gate current. The key difference between GTO and SCR is that a GTO can be turned off by applying a negative gate current. The structure and symbol of a GTO are shown below:
Major differences between GTO and SCR
| Gate Turn Off Thyristor (GTO) | Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) |
|---|---|
| Can be turn-on by applying a positive gate current and turned off by applying a high negative gate current. | Can be turn-on by applying a positive gate current and turned off only when the anode voltage drops below its holding voltage. |
| No commutation circuits are required. | Commutation circuit is required to turn off the SCR. |
| Symmetric GTOs have both forward and reverse conduction capabilities. | Reverse conduction is not possible. |
| Reverse voltage blocking capability is lesser compared to SCRs. | Higher reverse blocking voltage rating. |
Summary
GTO (Gate Turn-Off) and SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) are both types of power electronic devices used for controlling electrical power in various industrial and commercial applications. However, they have some key differences in terms of their operation and characteristics.
- GTO devices are thyristors that can be turned off by applying a negative voltage to their gate terminal. This allows them to be used in applications where the power needs to be turned on and off frequently and quickly.
- SCR devices, on the other hand, are not as easily turned off. They can be turned off only by reducing the current flowing through them to zero. This means that they are better suited for applications where power needs to be continuously flowing, such as in AC power control.
- GTOs have faster switching times compared to SCRs.
- GTOs have higher power losses in gate power and switching losses compared to SCRs.
- GTOs have a higher cost compared to SCRs.
- GTOs are used in high-frequency switching applications, such as inverters, while SCRs are used in low-frequency switching applications, such as in AC power control.
In general, GTOs are more versatile but also more complex and expensive, while SCRs are simpler and cheaper but with less flexibility.