Time-delay fuses can provide overload and short circuit protection while overcoming momentary current spikes. They are used for the protection of motors and transformers. The time-delay characteristics of these fuses typically allow them to be sized closer to the running rated full load current of the loads.
Time-delay fuses are also known as slow-blown fuses and dual-element time-delay fuses. They can be used for the protection of any kind of load: inductive or resistive. They are capable of overriding normal equipment current surges to reduce unnecessary fuse openings.
Operation of dual-element time-delay fuses
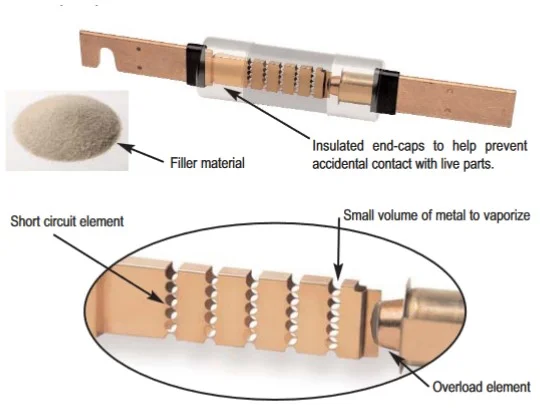
As the name indicates, the dual element time-delay fuse has a separate overload element and a short circuit element. The soldered joint along with a spring connection acts as the overload element. The short circuit protection part contains a copper conductor with portions for restricted current flow.
The restricted portion greatly reduces the short circuit let-through current through the fuse. These elements are placed inside a tube filled with arc quenching filler material. The tube prevents the contact accidental contact with the live parts.
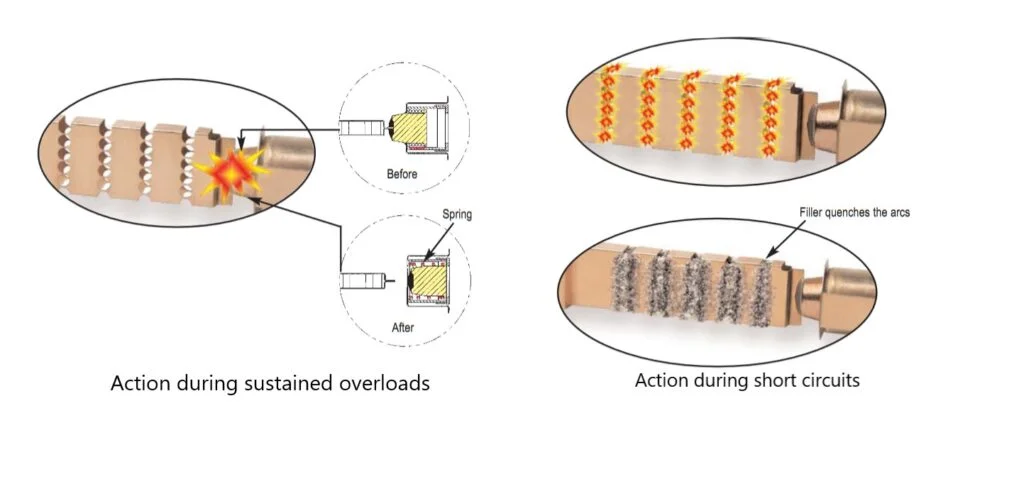
Nothing will happen to the fuse during momentary overloads of 100% to 200% of the fuse rating. In the case of sustained overloads, the solder joint melts and the spring pulls back the contact holder, thereby opening the interrupting circuit.
During short circuits, the small volume of metal in the restricted portions evaporates, and the arc commences. The arc quenching filler material surrounding the element extinguishes the arcing current. The filler material absorbs the heat produced by the arcs, fuses together, and creates an insulating barrier. This process helps in forcing the current to zero.
Advantages of slow-blown fuses
- Dual element fuses when used for motor protection can be sized close to the motor full load current, thereby reducing the cost.
- It can provide improved overload protection.
- These fuses can override normal current surges resulting from the equipment operations and avoid unnecessary fuse blown-outs.
- Provides a higher degree of short circuit protection in circuits with frequent current surges and overloads occur.
- Provide overload, short circuit, and ground fault protection to motors.
- Dual element time-delay fuses sized for overload protection of motor can also protect from the overloads caused due to single-phasing.
- If the thermal overload relay fails to operate, the dual-element fuses will act independently and thus provide “back-up” protection for the motor.
Application of time-delay fuses
- Used for the protection of motors and branch circuits.
- Used for the protection of transformers and other inductive loads.
- Can be used for the protection of noninductive loads also.
- It is recommended to use these fuses in power distribution feeders.
Additional information on how to select appropriate fuse: https://www.eaton.com/content/dam/eaton/products/electrical-circuit-protection/fuses/solution-center/bus-ele-tech-lib-motor-protection-tables.pdf