The objective is to analyze and understand the requirements of the materials used in an electric motor, understand the material requirement of each motor part, find out the materials utilized in the motor used for the study, and understand why that material is used.
The methodology used to study the materials used in an electric motor
For this study, we selected an industrial-grade motor manufactured by ABB, commonly utilized in the cement industry. The motor was dismantled and its parts were studied. To identify the materials used in the motor, we have referred to the datasheet provided by the manufacturer and engaged in discussions with expert personnel in ABB, as well as other suppliers of spare parts.
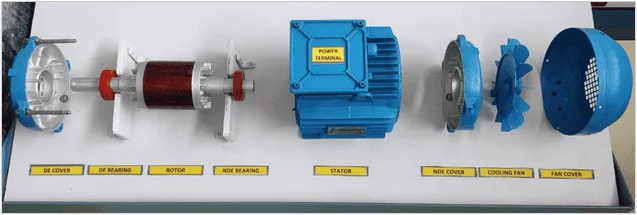
Exploded view of the motor under study
Parts identified:
- Frame
- Stator core
- Stator winding
- Rotor
- Shaft
- Coil insulation
- Slot insulation
- Power Terminals
- Fan
- Bearing
1. Motor Frame
A motor frame is a hollow external housing with a stator and a rotor disposed within the housing interior. At either end of the housing, end bells are present. The motor frame protects all the internal motor components.
Requirements of the materials used for the motor frame:
- The motor frame requires a high structural strength to support the stator.
- Low vibration transmission
- Resistance to corrosion
- Cost-effectiveness
The material in the motor studied: Grey cast Iron – GRS 150
Reason for using grey cast Iron for motor frame:
The other materials that can be used as motor frame material are aluminum and stainless steel. Here are a few reasons for choosing cast iron:
- Cast iron is cheaper than when compared to aluminum
- Excellent vibration damping capacity, being 25–100 times better than that of a 1080 steel.
- Cast iron has very good wear and tear resistance.
- Gray cast iron has better thermal conductivity and lower thermal expansion compared to other types of cast irons.
- Silicon content in the grey cast iron makes it resistant to corrosion.
2. Stator core
Inside the external frame, the stator core is attached. It serves as the support for the windings. It is assembled into a motor frame.
Requirements of the materials used for stator:
- The stator core must be capable of conducting the heat from the core to the external stator core. Hence it should have good thermal conductivity.
- Less hysteresis and eddy current losses.
- High magnetic permeability and low coercivity
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
Material used in the stator of the motor studied: Silicon steel laminations
Reason for using silicon steel lamination for the core:
- The magnetic permeability of silicon steel is high when compared to other materials.
- The coercivity, of silicon steel is low which makes rapid change in the magnetic field possible and reduces hysteresis.
- Laminations reduce the length of the eddy current path and help minimize the eddy current loss.
- Silicon steel has a low coefficient of thermal expansion.
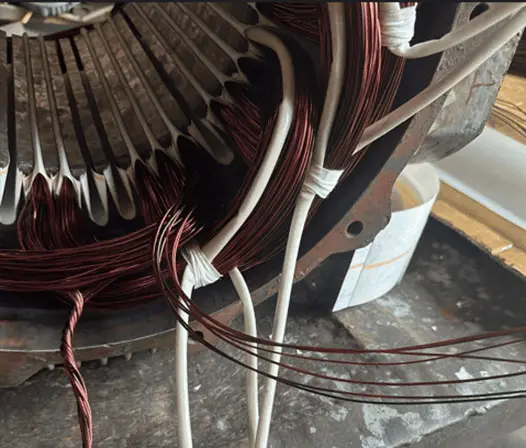
3. Stator winding
The stator winding is placed in the stator. These windings are responsible for generating the magnetic field necessary for the motor to function.
Requirements of the materials used for motor winding:
- High electrical conductivity
- High thermal conductivity
- Low coefficient of expansion to prevent deformation under high temperatures
The material in the motor studied: Copper-Dual enameled insulated.
Reason for using copper for coil:
The most used materials used as electrical conductors are copper and aluminum. Here is a comparison of why copper is used over aluminum:
- Copper has better electrical conductivity than aluminum.
- Copper has better electrical conductivity than aluminum.
- Copper has a lower coefficient of thermal expansion compared to aluminum.
Since copper has superior when it comes to key properties than aluminum, copper is used as a material for motor winding, despite its higher cost.
4. Rotor
The rotor is the rotating component of a motor. Nowadays the induction motor rotors do not carry any winding. A squirrel cage is used instead.
Requirements of the materials used for motor winding:
- The rotor material should have sufficient electrical conductivity.
- It should be able to withstand mechanical stresses and centrifugal forces.
- Lightweight and at the same time strong enough to spin the shaft in a loaded condition.
- Corrosion resistance.
The material in the motor studied: Pressure die-cast aluminum
Reason for using pressure die-cast aluminum for rotor cage:
- Die-cast aluminum has a high conductivity and strength-to-weight ratio at the same time.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Aluminium has relatively high thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat dissipation during motor operation.
5. Rotor Shaft
The motor shaft is attached to the rotor and extends outside the motor. It transfers the torque generated inside the motor to the load. The load is coupled to the shaft either directly or through a gearbox.
Requirements of the materials used for the shaft:
- The shaft should have high stiffness and rigidity.
- It should have high strength to handle the load.
- It should be fatigue-resistant
- Ductile
- Resistant to corrosion
- Resistant to heat
- Machinability
- Cost-effectiveness
Material in the motor studied: EN8 Steel
Reason for using stainless steel for shaft:
EN8 steel has a composition of 0.36% carbon, 0.1% – 0.4% silicon, 0.6% Magnesium, 0.05% phosphorous and 0.05% sulfur.
The following are the properties of the EN8 steel.
- EN8 steel has a High tensile strength
- Good wear resistance
- EN8 steel has excellent machinability
- It has very good hardness making it resistant to wear and tear
All these properties make it the suitable choice for the motor shaft.
6. Coil insulation
The coil in the winding is placed one over/next to the other. Hence to prevent intercoil short circuits. Coil insulation and the insulation for outgoing connections are extremely important for the safe operation of any motor.
Requirements of an insulating material:
- High dielectric strength
- High thermal insulation
- Resistance to aging and degradation.
High-temperature resistance.
The material in the motor studied: Epoxy fiberglass molded sleeve, Insulating varnish (ISONEL – 32-2, ELMO LUFT 1A Varnish)
Reason for using Epoxy fiberglass molded sleeve:
EN8 steel consists of 0.36% carbon, 0.1% – 0.4% silicon, 0.6% magnesium, 0.05% phosphorous, and 0.05% sulfur.
- Epoxy fiberglass sleeves and insulating varnish exhibit a remarkably high dielectric strength.
- The epoxy fiberglass sleeve has very good mechanical strength and can sustain mechanical stresses and vibrations during motor operation.
- Epoxy fiberglass is resistant to corrosion, rust, and oxidation, hence it can be used in motors in corrosive environments.
- EN8 steel is chemically inert.
- It is resistant to wear and tear.
7. Coil-slot insulation
The winding coils are placed in the stator slot and hence apart from the insulation provided between the coils, the coil and the slot also need to be isolated.
Requirements of a coil-slot insulating material:
- The insulator used in the slot should be lightweight and thin.
- It should possess high-temperature resistance.
- High dielectric strength.
- Mechanical strength.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- Resistance to aging and degradation.

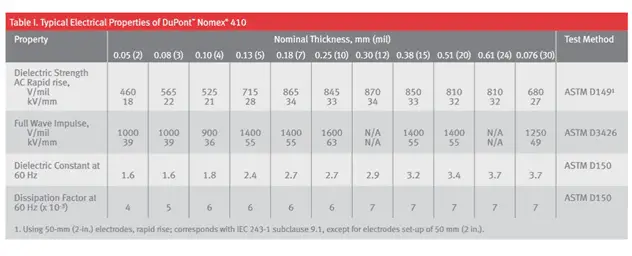
Material used in the motor studied: Nomex paper
Reason for using Nomex paper as the insulation for the paper:
Nomex paper has the following properties:
- Nomex paper can withstand upto220 degrees Celsius.
- It is thin and has very high dielectric strength and can withstand up to 870kV/mm.
- It has a low thermal conductivity
- Nomex paper exhibits good tear resistance.
- It has a high mechanical strength that can support the windings and is capable of keeping the windings in place, even under mechanical stress and vibration.
8. Power terminals
The power supply to the motor is connected to power terminal blocks within the terminal box of the motor. Typically, the terminal box is made up of the same material as the material of the motor frame (in the motor we studied, it is grey cast iron).
Terminal blocks are insulated from the motor frame using a ceramic base.
Requirements of the materials used for Power terminals:
- Sufficient electrical conductivity
- Ability to withstand high starting currents
- Robustness
- Corrosion resistance
Material used in the motor studied: Stainless steel bolts with zinc and chromium plating
Reason for using Stainless steel bolts:
- For short distances (such as the length of a bolt) with higher cross sections, stainless steel provides sufficient conductivity.
- Yellow chromate prevents the zinc from corroding and increases the overall protection of the finish.
- High strength
9. Cooling Fan
A cooling fan is fitted to the motor shaft and rotates along with it. It blows air to the outer frame and facilitates the cooling of the motor.
Requirements of the materials used for cooling fan:
The basic requirements of the fan are to have sufficient strength and be lightweight.
The material used in the motor studied: Polypropylene with 20% reinforced glass
10. Bearing
The rotor shaft is supported on the stator casing with the help of a bearing.
Requirements of the materials used for bearing:
- The bearing material should be able to withstand heavy loads.
- Should be durable and wear-resistant.
- Corrosion resistant.
- High Fatigue Strength
Material used in the motor studied: Chromium Steel
Reason for using chromium steel for making bearings:
Chromium steel consists of 10-30% of chromium and has the following properties.
- Chromium steel has high load-withstanding capacity
- Chromium steel exhibits Resistance to wear.
- High fatigue strength.
- It is resistant to corrosion.