Metal halide (MH) lamp
 Metal halide (MH) lamp provides high efficiency, long service life and excellent colour rendition. It consists of an arc tube enclosed in a glass chamber made up of borosilicate glass. Arc tube is also called as discharge tube or “burner”. The arc tube consists of argon gas, mercury and metal salts such as sodium iodide. They operate at higher temperatures and pressures.
Metal halide (MH) lamp provides high efficiency, long service life and excellent colour rendition. It consists of an arc tube enclosed in a glass chamber made up of borosilicate glass. Arc tube is also called as discharge tube or “burner”. The arc tube consists of argon gas, mercury and metal salts such as sodium iodide. They operate at higher temperatures and pressures.Ballast is used to supply a high starting voltage. The ballast also regulates the lamp starting current and lamp operating current. (more…)
How refrigerators work?
How do Fuel Cells Work?
Fuel Cell Fuel cells cleanly and efficiently convert chemical energy from hydrogen-rich fuels into electrical power and usable high-quality heat in an electrochemical process that is virtually absent of pollutants.…
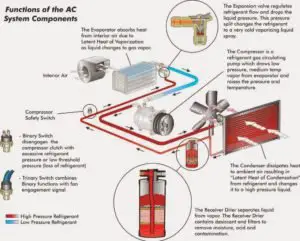
How does a car Air Conditioner work?
Air conditioning works continuously and has refrigerant continually circulating around a sealed system. Most automotive A/C systems are made up of six main components:-
- Compressor and mounting brackets
- Condenser
- Receiver/ drier
- Expansion Valve
- Evaporator
- Hose & fittings
The easiest way to explain how the system works is to trace the refrigerant as it flows through the system:- (more…)
How does a speaker work?
Speaker is a device which converts electrical signal into sound waves. By
its property, sound is made when an object makes the particles around it
vibrate. These vibrations travel through the air, and reach our ears. Our brain
interprets this motion as sound. The amplitude of the waves corresponds to the volume level we hear and the frequency decides the nature of sound. (more…)
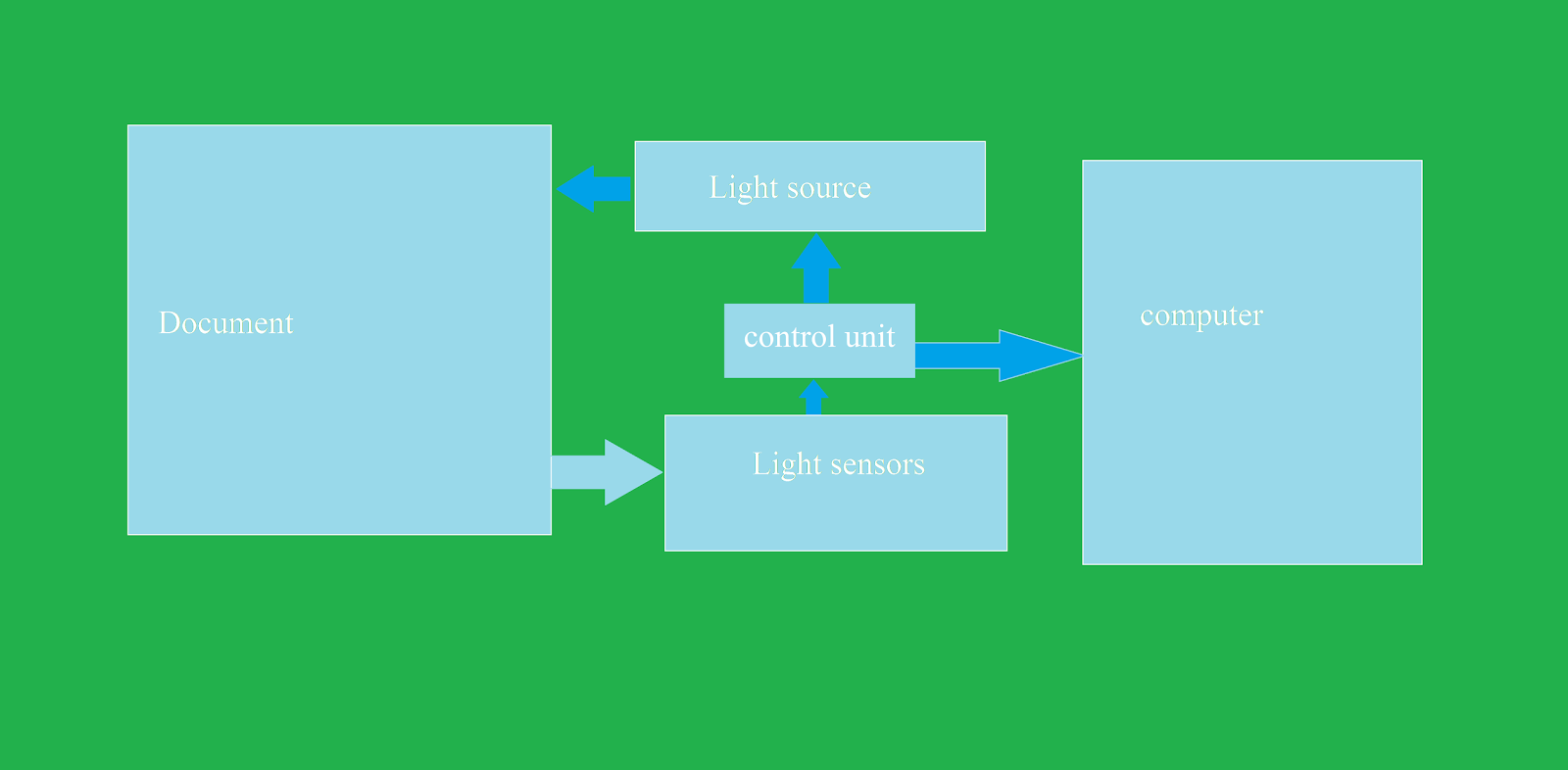
How does a scanner work?
Scanners are used to create a soft copy of available photos and documents.
When we open the scanner we can see a glass plate. We have to place the
document that we need to scan over the glass plate. (more…)
Optical Mouse
Fluorescent lamps
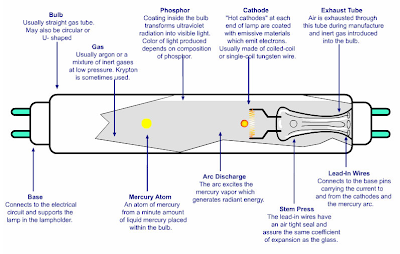
Fluorescent lamps are commonly used every where. These lamps are more energy efficient than ordinary incandescent light bulbs. (more…)
How Does an incandescent Bulb Work?
In an incandescent light bulb, light is produced by the heating of filament. It has a carbon-based filament in the center of the bulb connected to the two terminals and maintained at vacuum glass chamber. This filament has a high resistance to electric current. (more…)