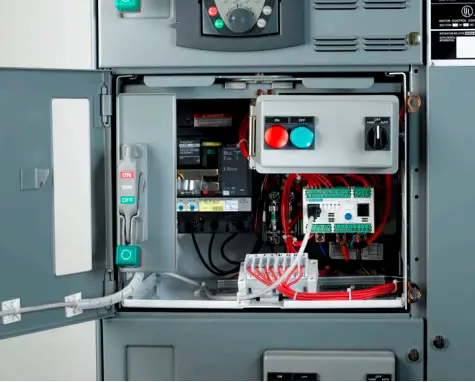
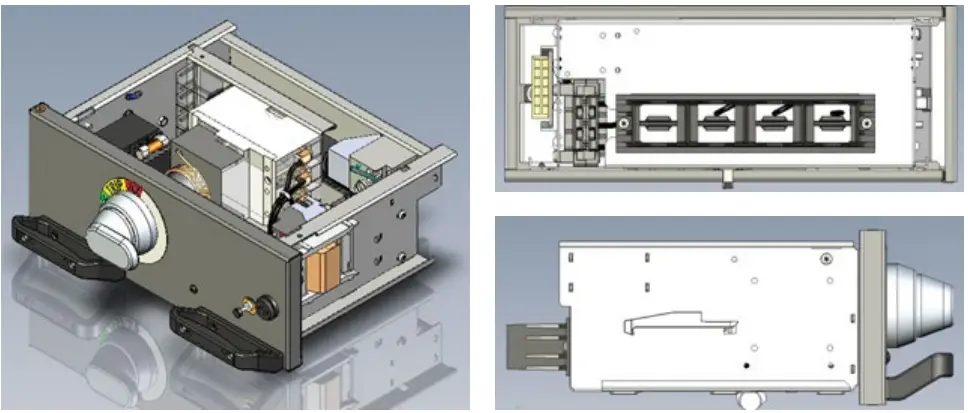
Hundreds are electrical motors are used in modern-day industries for process automation and control. To control those motors, motor control centers or MCC panels are needed. They contain circuit breakers and motor starters to start, stop and run motors effectively. In this article let us discuss the structure types and features of motor control centers in detail.
What is an MCC panel?
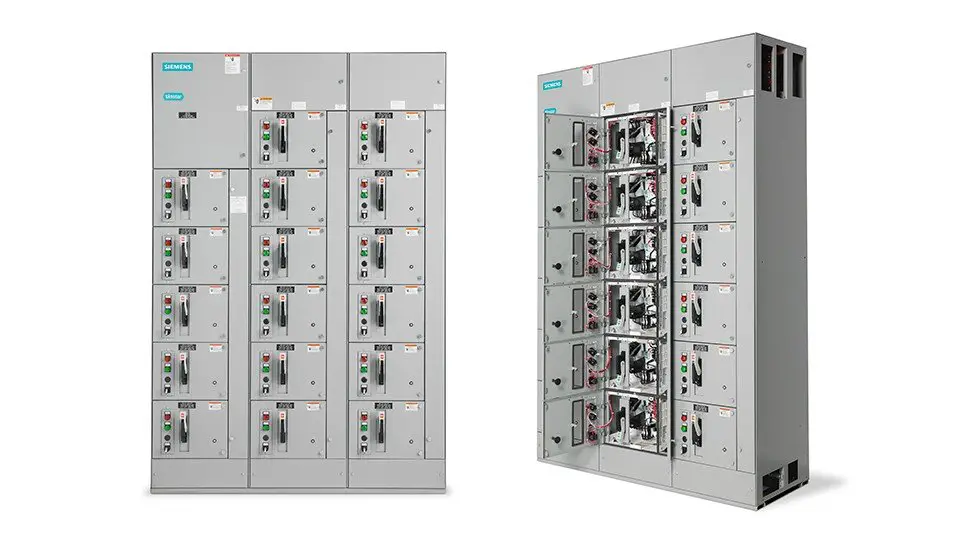
A Motor control center, commonly known as an MCC panel, is a group of combination motor starters, branch feeder devices, and lighting panelboards, each mounted in an individual isolated compartment with its own cover. It is a free-standing structure, consisting of a common busbar arrangement to distribute power to each compartment and a network of wireways to accommodate outgoing loads and control wirings.
A typical MCC consists of the main feeder along with feeder controls, indications, current and voltage measurements, and several combination starters. The operating handles, indications, push buttons, and measurement devices are mounted on the door of each compartment.
The combination starter compartments contain motor starters, circuit breakers, indication lamps, push buttons, and metering devices. It may also contain variable frequency drives and soft starters. In some cases, motor control centers may also contain compartments for power feeders and PLCs.
Types of motor control centers
Based on the compartment arrangement, they can be classified into Fixed and Withdrawable compartmented motor control centers.
The compartmental arrangements are made in order to ensure adequate isolation between each motor starter and between the starters and the operators. In a fixed construction the compartments and their components are permanently attached to the structure. Any repair or maintenance to the components in any compartment requires the main incomer to be opened. All the outgoing cables are connected to fixed terminal blocks or busbar contacts.
In a withdrawable construction, starter compartments can be withdrawn and re-inserted back into their structure. The compartments containing starters are directly inserter to the compartments slots. Plugin contacts are present for power and control contacts. Separate sets of terminals are present outside the compartment for the connection of all the outgoing cables. No provision for external cable terminations is provided within the withdrawable compartment.
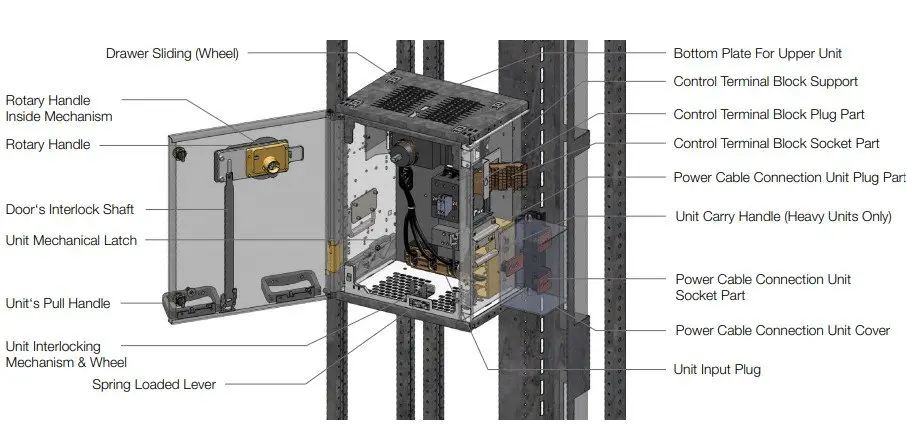
The withdrawable units come with a possibility of test position. This position allows testing of control circuits in the motor starter present in the compartment by connecting a separate control power source to the unit. The withdrawable units have to be fully inserted to make proper contact with the fixed contacts.
The following are the basic components present in a typical DOL or star-delta motor starter compartment:
- Circuit breaker for short circuit protection.
- Contactors for motor switching.
- Protection relays such as overload, phase fault, phase sequence, phase monitoring, and under/over voltage relays.
- Push buttons and pilot lamps.
- Voltage and current measurement devices.
- Terminal blocks.
Intelligent motor control centers (iMCC)
iMCCs make use of intelligent motor controllers to combine motor protection and control functions. It enables live monitoring and fault diagnosis of motor starters. Motor controllers can communicate with the PLC or DCS systems through popular network protocols such as CANopen, DeviceNet™, Ethernet, Modbus, PROFIBUS, etc. Monitoring of critical data can help in effective motor control all the time and problems can be fixed proactively. Real-time access to the data and the availability of past data can allow simplified diagnostics and reduced downtime. Popular intelligent motor controllers available in the market are ABB’s UMC, Siemens Simcode Pro, and Schneider TeSys T.
Low-voltage motor control centers are available at a voltage rating up to 600V and medium voltage assemblies are available up to a rating of 15000 V.
Useful reference: https://selinc.com/api/download/102532/
Also read: Ingress protection rating or IP rating (IEC 60529)
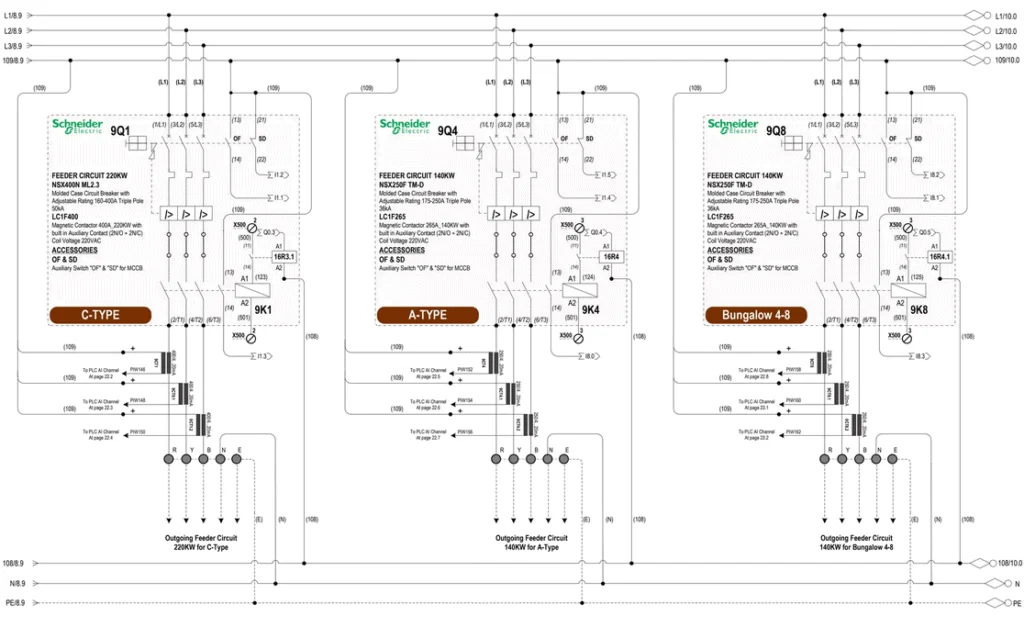
Download a sample MCC panel drawing from here: Efficient Load Management System (ELMS) with ATS_AMF Generator Control Drawing